Derivations for moments of univariate normal distribution#
Standard Normal#
Expectation#
\[\begin{split}
\begin{array}{c}
X{\sim} p(x) \\
\sim \mathcal{N}(0,1) \\
=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}}e^{(-1 / 2) x^{2}} \\
E_{X}[x]=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}}e^{(-1 / 2) x^{2}} \cdot x dx
\end{array}
\end{split}\]
Solve indefinite integral, $\( \begin{array}{l} I=\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} e^{-x^{2} / 2} \cdot x d x \\ y=\frac{-x^{2}}{2} \Rightarrow d y=-x d x \\ \therefore I=\int \frac{-1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} e^{y} d y=\frac{-1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} \int e^{y} d y=\frac{-1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} e^{y} \end{array} \)\( Substitute back \)\( I=\frac{-1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} e^{-x^{2} / 2} \)\( Definite integral is \)\left.\frac{-1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} e^{-x^{2}}\right|_{-\infty} ^{\infty}=\frac{-1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}}\left(e^{-\infty}-e^{-\infty}\right)=0$
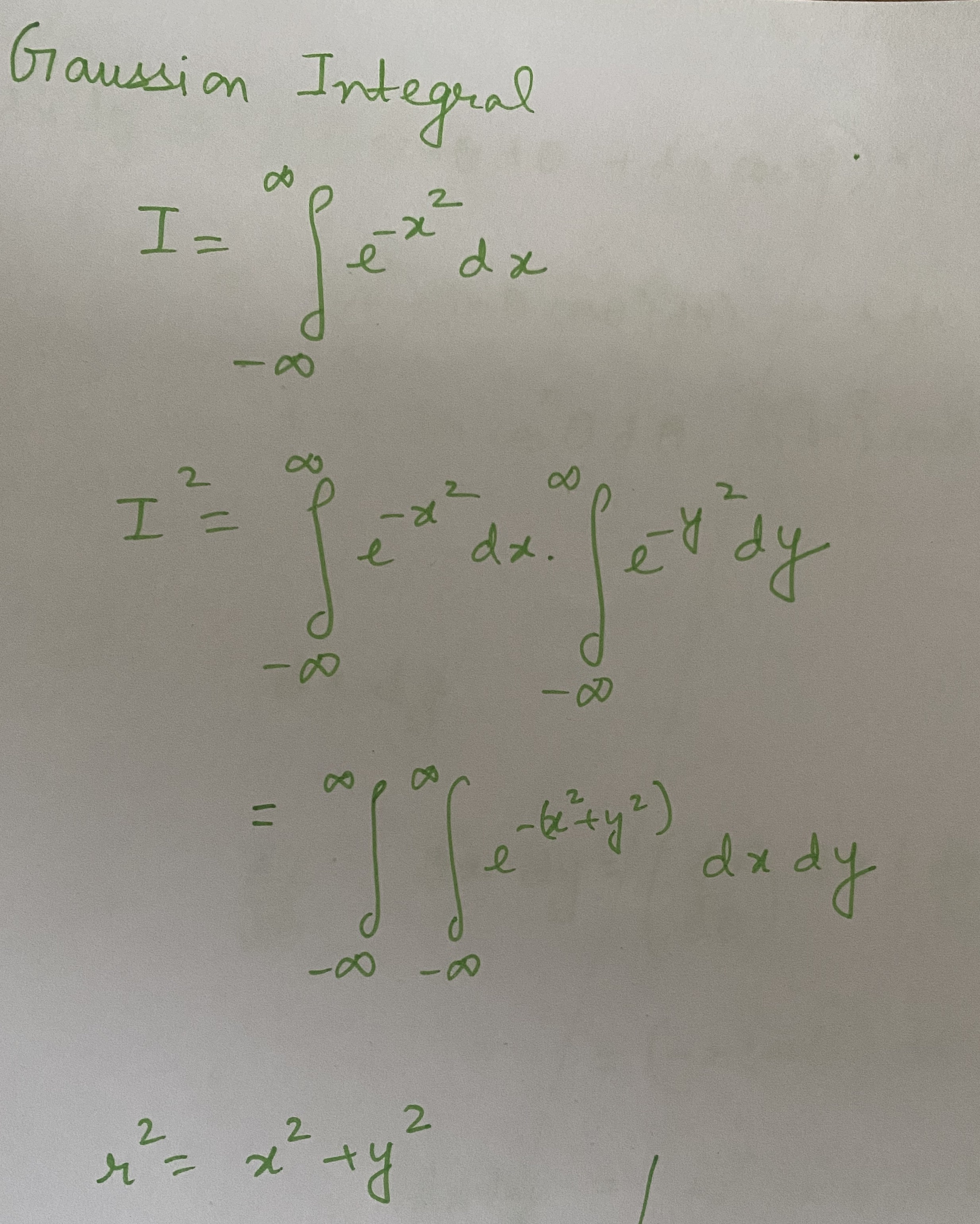
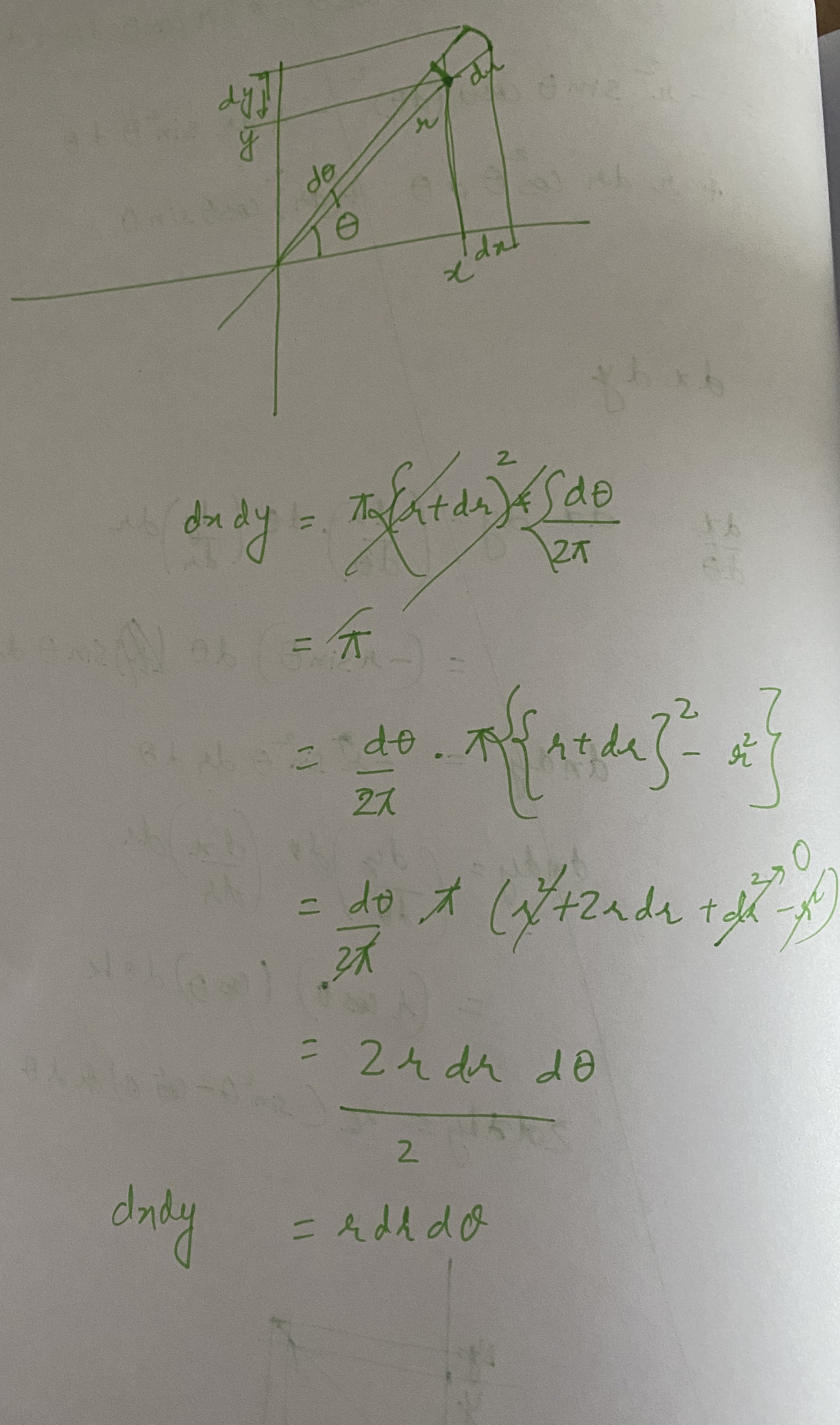
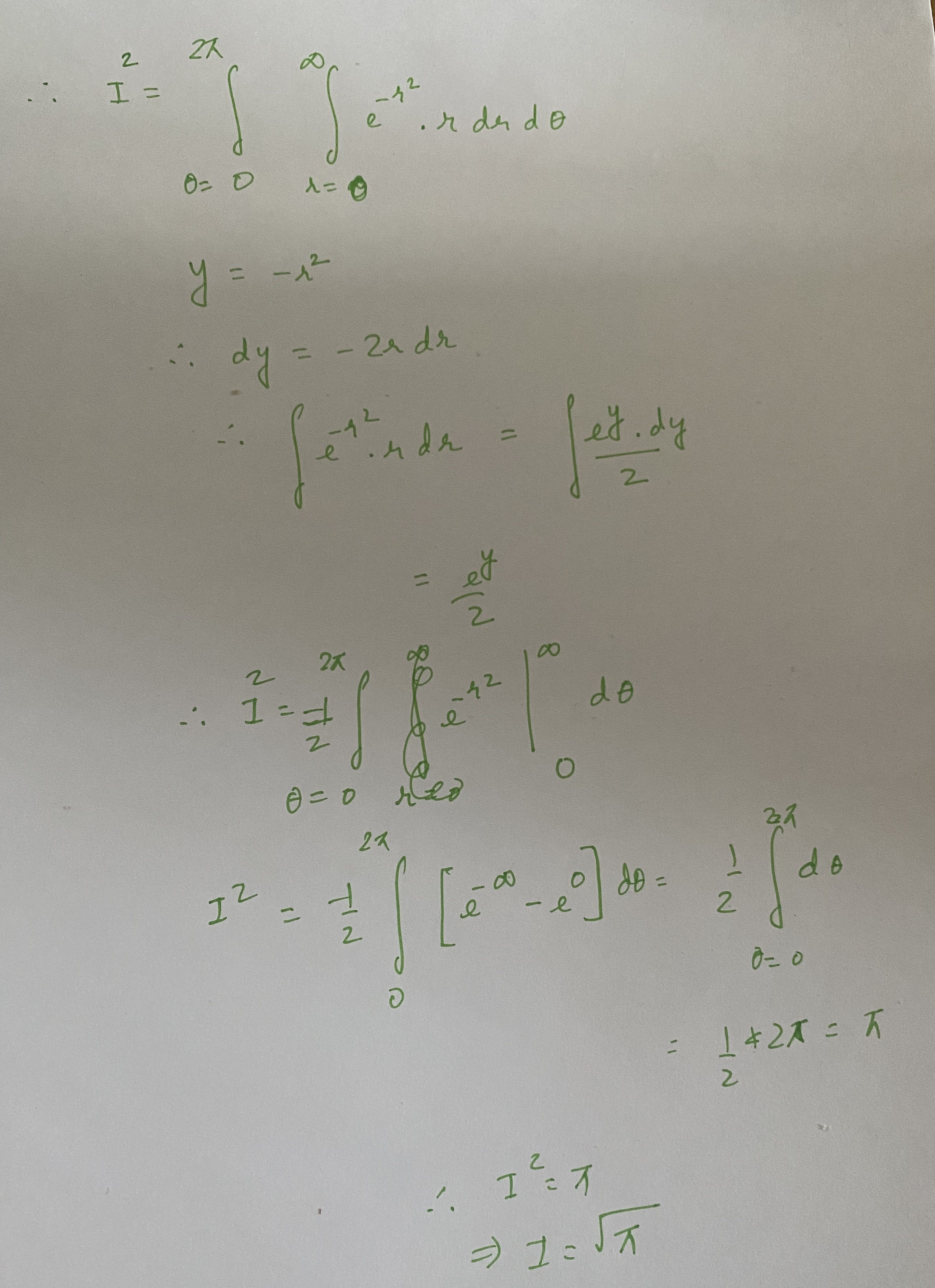
Variance#
Affine Transformation of Standard Normal#
References
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zbHRUnR9F-4 (Very detailed!)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l27xKSNad2Y (Very intuitive double integral explanation)

