Logistic Regression using PyTorch distributions
Contents
Logistic Regression using PyTorch distributions¶
Basic Imports¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
dist =torch.distributions
sns.reset_defaults()
sns.set_context(context="talk", font_scale=1)
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format='retina'
Generative model for logistic regression¶
x = dist.Normal(loc = torch.tensor([0., 0.]), scale=torch.tensor([1., 2.]))
x_sample = x.sample([100])
x_sample.shape
x_dash = torch.concat((torch.ones(x_sample.shape[0], 1), x_sample), axis=1)
theta = dist.MultivariateNormal(loc = torch.tensor([0., 0., 0.]), covariance_matrix=0.5*torch.eye(3))
theta_sample = theta.sample()
p = torch.sigmoid(x_dash@theta_sample)
y = dist.Bernoulli(probs=p)
y_sample = y.sample()
plt.scatter(x_sample[:, 0], x_sample[:, 1], c = y_sample, s=40, alpha=0.5)
sns.despine()
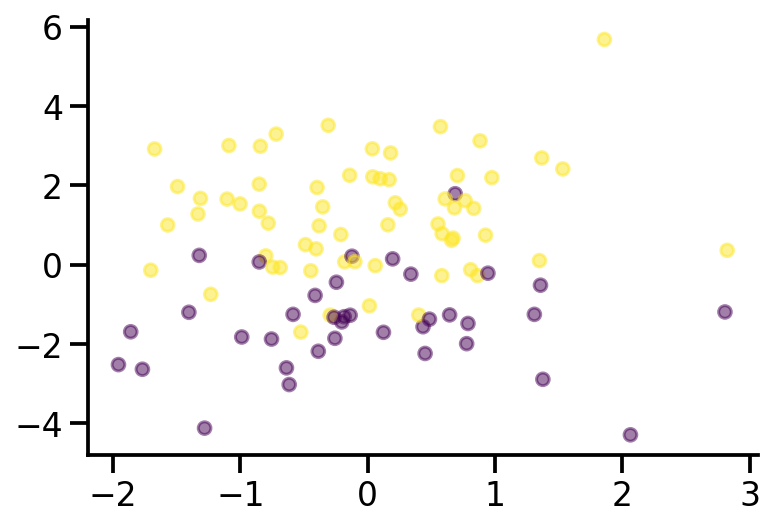
theta_sample
tensor([ 0.6368, -0.7526, 1.4652])
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
lr_l2 = LogisticRegression()
lr_none = LogisticRegression(penalty='none')
lr_l2.fit(x_sample, y_sample)
lr_none.fit(x_sample, y_sample)
LogisticRegression(penalty='none')
def plot_fit(x_sample, y_sample, theta, model_name):
# Retrieve the model parameters.
b = theta[0]
w1, w2 = theta[1], theta[2]
# Calculate the intercept and gradient of the decision boundary.
c = -b/w2
m = -w1/w2
# Plot the data and the classification with the decision boundary.
xmin, xmax = x_sample[:, 0].min()-0.2, x_sample[:, 0].max()+0.2
ymin, ymax = x_sample[:, 1].min()-0.2, x_sample[:, 1].max()+0.2
xd = np.array([xmin, xmax])
yd = m*xd + c
plt.plot(xd, yd, 'k', lw=1, ls='--')
plt.fill_between(xd, yd, ymin, color='tab:blue', alpha=0.2)
plt.fill_between(xd, yd, ymax, color='tab:orange', alpha=0.2)
plt.scatter(*x_sample[y_sample==0].T, s=20, alpha=0.5)
plt.scatter(*x_sample[y_sample==1].T, s=20, alpha=0.5)
plt.xlim(xmin, xmax)
plt.ylim(ymin, ymax)
plt.ylabel(r'$x_2$')
plt.xlabel(r'$x_1$')
theta_print = np.round(theta, 1)
plt.title(f"{model_name}\n{theta_print}")
sns.despine()
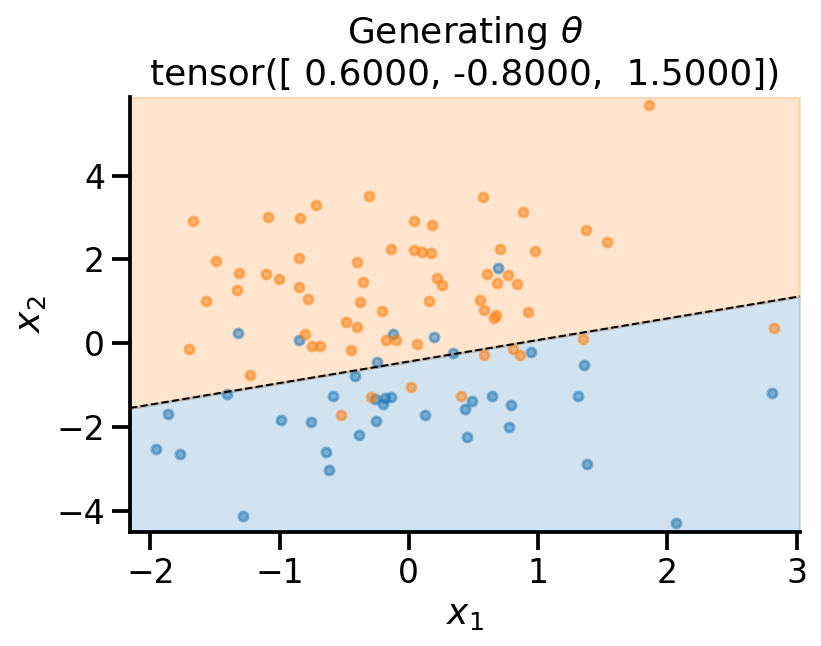
plot_fit(
x_sample,
y_sample,
theta_sample,
r"Generating $\theta$",
)
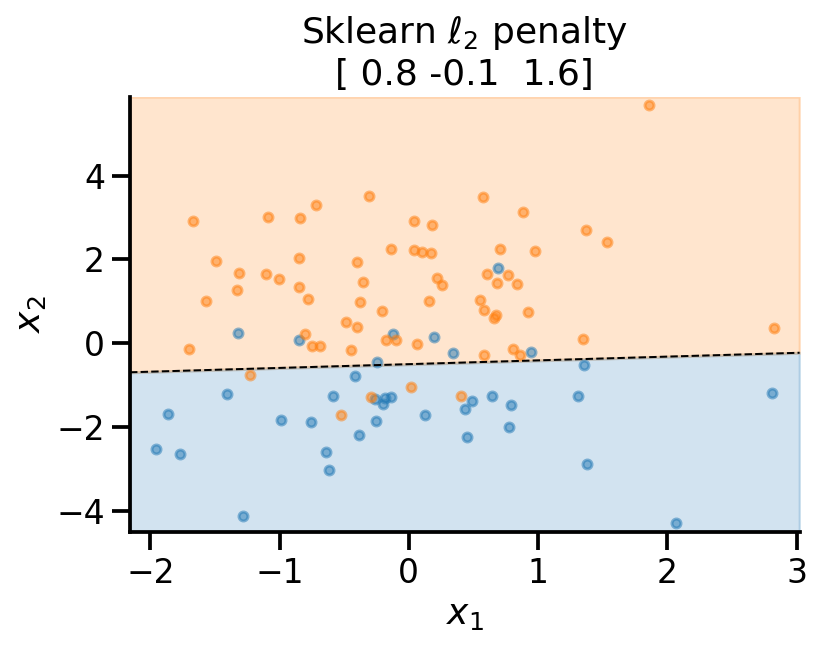
plot_fit(
x_sample,
y_sample,
np.concatenate((lr_l2.intercept_.reshape(-1, 1), lr_l2.coef_), axis=1).flatten(),
r"Sklearn $\ell_2$ penalty ",
)
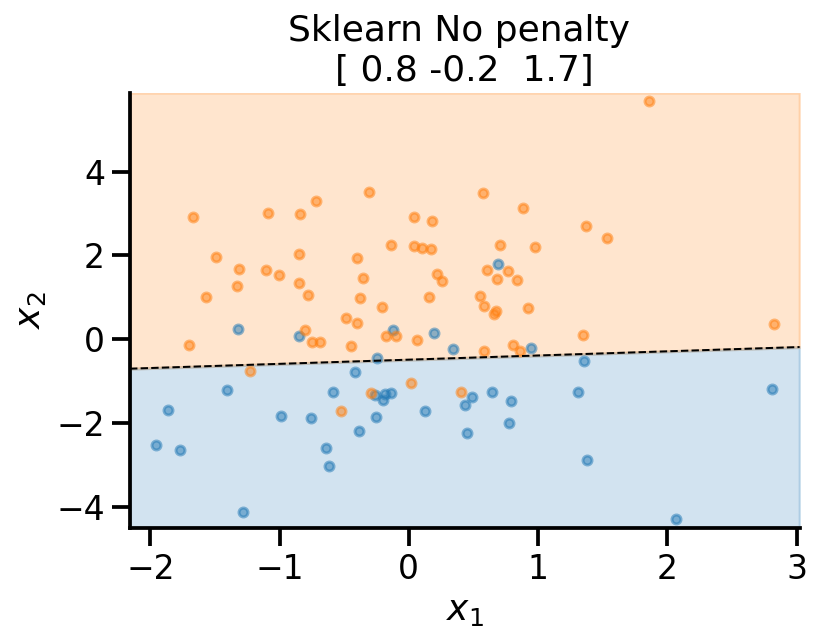
plot_fit(
x_sample,
y_sample,
np.concatenate((lr_none.intercept_.reshape(-1, 1), lr_none.coef_), axis=1).flatten(),
r"Sklearn No penalty ",
)
MLE estimate PyTorch¶
def neg_log_likelihood(theta, x, y):
x_dash = torch.concat((torch.ones(x.shape[0], 1), x), axis=1)
p = torch.sigmoid(x_dash@theta)
y_dist = dist.Bernoulli(probs=p)
return -torch.sum(y_dist.log_prob(y))
neg_log_likelihood(theta_sample, x_sample, y_sample)
tensor(33.1907)
theta_learn_loc = torch.tensor([1., 1., 1.], requires_grad=True)
neg_log_likelihood(theta_learn_loc, x_sample, y_sample)
plot_fit(
x_sample,
y_sample,
theta_learn_loc.detach(),
r"Torch without training",
)
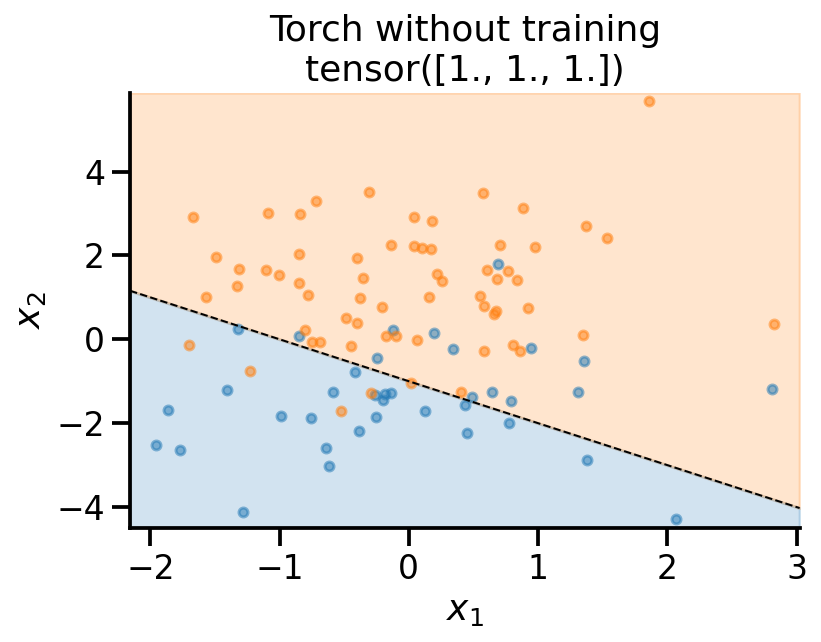
theta_learn_loc = torch.tensor([0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True)
loss_array = []
loc_array = []
opt = torch.optim.Adam([theta_learn_loc], lr=0.05)
for i in range(101):
loss_val = neg_log_likelihood(theta_learn_loc, x_sample, y_sample)
loss_val.backward()
loc_array.append(theta_learn_loc)
loss_array.append(loss_val.item())
if i % 10 == 0:
print(
f"Iteration: {i}, Loss: {loss_val.item():0.2f}"
)
opt.step()
opt.zero_grad()
Iteration: 0, Loss: 69.31
Iteration: 10, Loss: 44.14
Iteration: 20, Loss: 35.79
Iteration: 30, Loss: 32.73
Iteration: 40, Loss: 31.67
Iteration: 50, Loss: 31.25
Iteration: 60, Loss: 31.08
Iteration: 70, Loss: 31.00
Iteration: 80, Loss: 30.97
Iteration: 90, Loss: 30.95
Iteration: 100, Loss: 30.94
plot_fit(
x_sample,
y_sample,
theta_learn_loc.detach(),
r"Torch MLE",
)
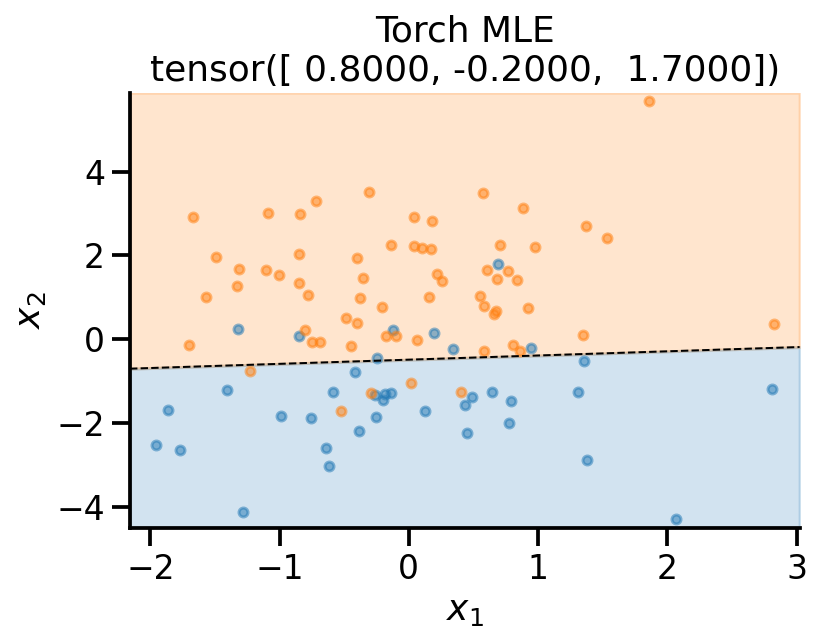
MAP estimate PyTorch¶
prior_theta = dist.MultivariateNormal(loc = torch.tensor([0., 0., 0.]), covariance_matrix=2*torch.eye(3))
logprob = lambda theta: -prior_theta.log_prob(theta)
theta_learn_loc = torch.tensor([0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True)
loss_array = []
loc_array = []
opt = torch.optim.Adam([theta_learn_loc], lr=0.05)
for i in range(101):
loss_val = neg_log_likelihood(theta_learn_loc, x_sample, y_sample) + logprob(theta_learn_loc)
loss_val.backward()
loc_array.append(theta_learn_loc)
loss_array.append(loss_val.item())
if i % 10 == 0:
print(
f"Iteration: {i}, Loss: {loss_val.item():0.2f}"
)
opt.step()
opt.zero_grad()
Iteration: 0, Loss: 73.11
Iteration: 10, Loss: 48.06
Iteration: 20, Loss: 39.89
Iteration: 30, Loss: 37.01
Iteration: 40, Loss: 36.10
Iteration: 50, Loss: 35.78
Iteration: 60, Loss: 35.67
Iteration: 70, Loss: 35.64
Iteration: 80, Loss: 35.62
Iteration: 90, Loss: 35.62
Iteration: 100, Loss: 35.62
plot_fit(
x_sample,
y_sample,
theta_learn_loc.detach(),
r"Torch MAP",
)
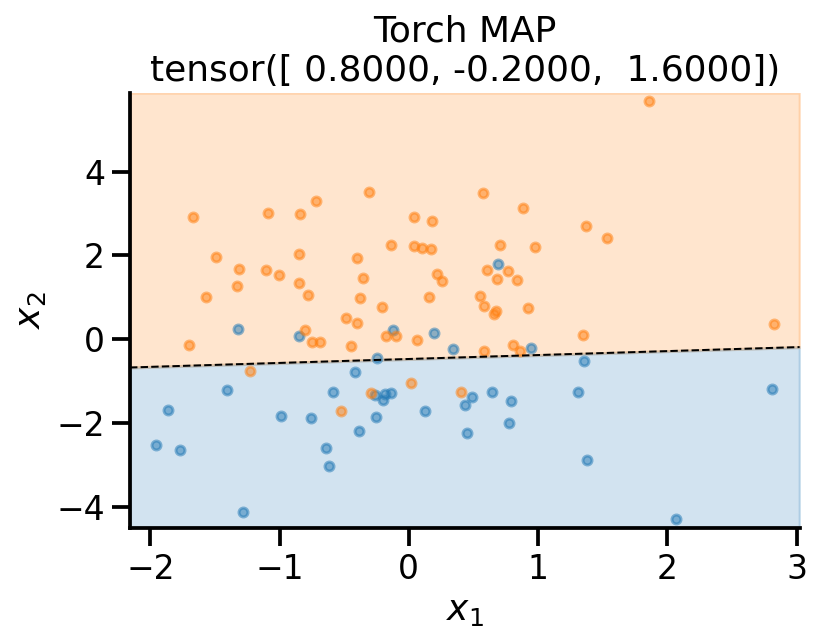
References¶
Plotting code borrwed from here: https://scipython.com/blog/plotting-the-decision-boundary-of-a-logistic-regression-model/
